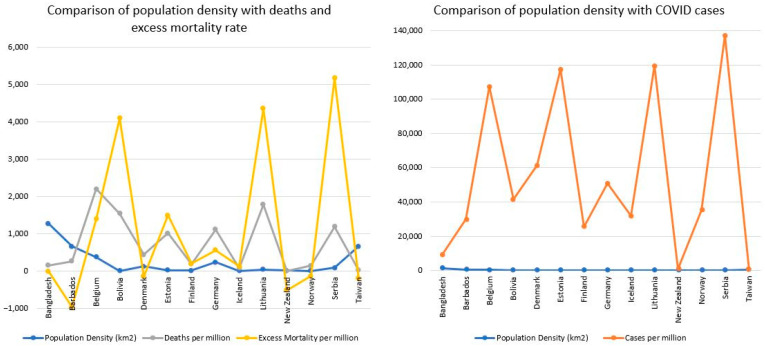
A study analyzed 194 countries, revealing that those led by women generally had better pandemic outcomes compared to male-led nations.
The paper delves into the responses of female leaders from 14 nations, such as New Zealand, Germany, and Denmark, to the COVID-19 crisis by September 2021, examining the effective strategies such as the timing and length of school and work lockdowns employed to control the spread of the virus and highlights how qualities like empathy, community-focused leadership, and communication style helped in fostering trust among citizens during challenging times.
Impact of Leadership Gender on COVID-19 Mitigation Policies
General findings:
- Female leaders tended to implement lockdowns earlier, resulting in about half as many deaths on average, suggesting female leaders are more cautious regarding public health but also willing to take economic risks when necessary.
- Female leadership contributed positively through focused messaging toward vulnerable populations like low-income individuals or refugees, suggesting that fostering collaboration and understanding among diverse groups, along with prioritizing inclusive leadership styles, may be essential for building resilience in communities facing future challenges.
- Female leadership played a significant role in effective crisis management. Women-led administrations often showcased empathy, clear communication skills, adaptability under pressure—qualities that improved community response during crisis.
Specific strategies:
- Bangladesh implemented strict measures like closing public transport for 502 days and stay-at-home orders for 553 days.
- Belgium offered extensive financial help lasting 574 days.
- Germany had long school closures (583 days) and strong protection efforts for the elderly.
- Taiwan excelled with robust testing policies, contact tracing initiatives running up to around 619–638 days while having minimal workplace disruptions (139 days).
- Taiwan excelled at using social media to combat stress and spread accurate information, while others struggled with these efforts underscoring how leaders’ attitudes towards the disease played out wuth those who took it seriously gained more citizen trust compared to dismissive leaders.
Overall, both informed public messaging and capable leadership significantly influenced how well different countries managed pandemic challenges.
Ultimately, these factors underscored the importance of inclusive governance and diverse perspectives in fostering resilience and promoting effective crisis management.
Female Leaders and Pandemic Management: A Path to Gender Equity
This study highlights how female leaders effectively managed the COVID-19 pandemic, challenging stereotypes about women's abilities.
- Their success could reshape societal views on gender roles, promoting more inclusive practices in government and leadership.
- By demonstrating strong crisis management skills, these women leaders may inspire others to pursue leadership positions. ceeating better representation of women in decision-making roles and influence policy priorities toward collaboration and inclusiveness.
- The actions of female leaders during the pandemic have implications for global public health cooperation among countries. Effective strategies from female leaders not only address immediate crises but also promote long-term readiness for future challenges while advocating equitable distribution of domestic responsibilities between genders.
- The research suggests that further studies should explore female leadership's effectiveness alongside broader impacts like economic downturns or mental health issues stemming from lockdown measures.
- By fostering diverse leadership styles and perspectives, organizations can better navigate challenges and drive sustainable progress.
Source ▼
 PMC home page*Correspondence: eozdenrlmemphis.edu; Tel.: +1-901-438-3461
PMC home page*Correspondence: eozdenrlmemphis.edu; Tel.: +1-901-438-3461